Presenter: Priya Krishna, MD, MS, FACS
Presenter: Priya Krishna, MD, MS, FACS
Director of Voice & Swallowing Center at Loma Linda Medical Center
Dr. Krishna is board certified in otolaryngology and completed a prestigious two year fellowship in Laryngology and Care of the Professional Voice at the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center under Clark Rosen, M.D., F.A.C.S. Prior to this she completed a residency in Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery at the Southern Illinois University School of Medicine. Dr. Krishna served as faculty in the Department of Otolaryngology at the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center from 2006 to 2011 while concurrently completing a Master of Science degree in Clinical Research. Dr. Krishna specializes in surgical and medical care of voice, airway and swallowing disorders including phonomicrosurgery of benign and early malignant lesions of the vocal folds, office laser based procedures for laryngeal pathology, endoscopic treatment of airway stenosis and neurological disorders of the larynx. She has a special research interest in treatment of vocal fold scarring and related wound healing disorders of the larynx and has been funded extramurally (including federal) for her work in the past.
CASE: 23 y/o female swim instructor presents with complaints of trouble projecting voice, vocal fatigue with use and progression over 6 months. Voice rest is helpful.
PMH: systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura, antiphospholipid antibody positive, hx of pulmonary embolism
ROS: unremarkable except for HPI
ALLERGIES: humira, rituximab
MEDS: abatacept, calcium carbonate, ferrous sulfate, plaquenil, levonorgestrel, prednisone, warfarin
SOCIAL: non smoker, social ETOH, swim instructor with high voice demands.
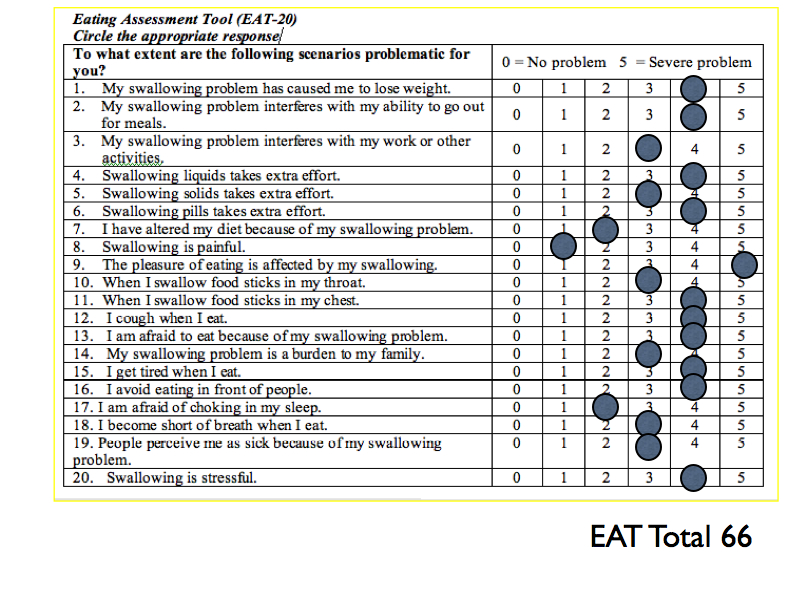
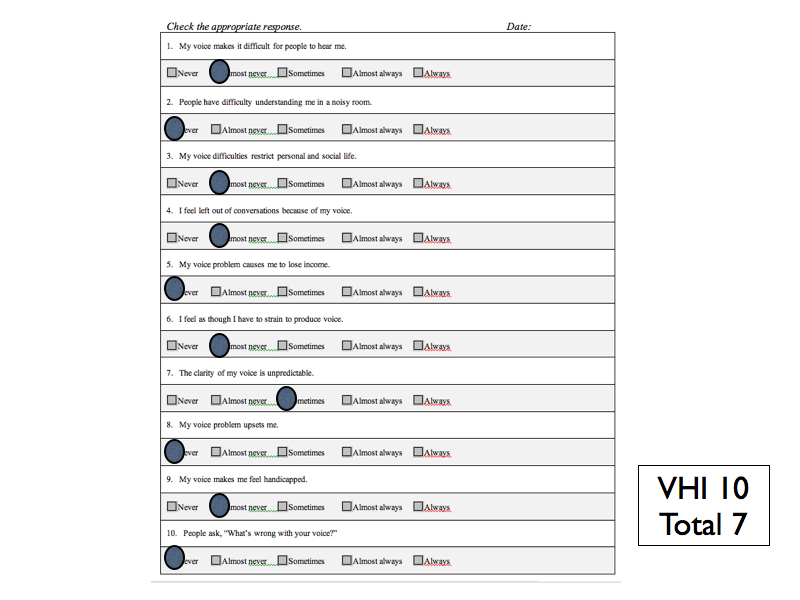
SELF RATINGS: Voice Handicap Index-10 = 33 Reflux Symptom Index = 9
PHYSICAL EXAM: hoarse voice, scant intranasal mucus, otherwise unremarkable
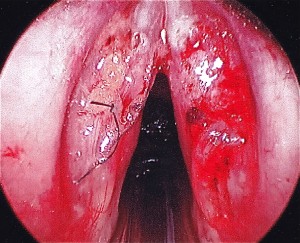
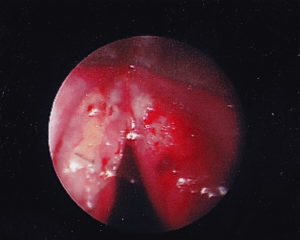
STROBE: Bilateral mid membranous vocal fold lesions with decreased mucosal wave and amplitude. Hourglass glottal closure. Left VF lesion larger in size than right vocal fold lesion. Bilateral vocal fold erythema, edema and moderate varices. Normal mobility of bilateral vocal folds.
TX RECOMMENDED: Microflap excision of bilateral vocal folds lesions and bilateral fat implantation followed by voice therapy. Second option was injection of vocal folds with steroids, which may take multiple treatments but can also be effective. Pt desired a one time surgical treatment.
SURGERY: Pt underwent microsuspension direct laryngoscopy with microflap excision of bilateral vocal fold lesions, abdominal fat harvest with bilateral fat implantation.
 |
 |
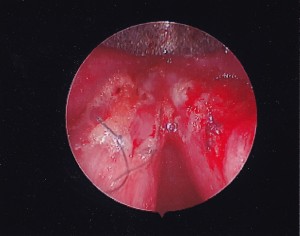 |
OUTCOME: Pathology c/w vocal fold cysts with elements of rheumatoid nodules (multinucleated giant cells).
1st POST-OP SELF-RATINGS: Voice Handicap Index -10 = 38 Reflux Symptom Index = 7
STROBE: Exam indicates healing vocal folds with reaction to fat and suture but good augmentation both vocal folds; lack of mucosal wave bilateral and “splinting” posture of larynx.
2nd POST-OP SELF-RATINGS: Voice Handicap Index -10 = 29 Reflux Symptom Index =not completed
STROBE: Decreased edema and erythema of bilateral vocal folds, decreased mucosal wave. Much improved from previous postoperative exam.
FOLLOW-UP: Continues to improve with time and voice therapy.

Professor and Director of Voice & Swallowing Center at UC Davis Medical Center
Dr. Belafsky’s primary clinical interests are the comprehensive diagnosis and management of voice, swallowing, and airway disorders. As Medical Director of the Voice and Swallowing Center at UC Davis, Dr. Belafsky treats a wide array of laryngeal and esophageal disorders. These disorders include but are not limited to vocal fold paralysis and paresis, vocal fold dysfunction, laryngopharyngeal reflux, chronic cough, and dysphagia caused by stroke, ALS, Zenker’s diverticulum, esophageal motility disorders, Parkinson’s disease, and swallowing problems suffered as a consequence of the treatment of head and neck cancer. Dr. Belafsky has pioneered minimally invasive treatments of voice and swallowing disorders. Minimally invasive in-office procedures performed by Dr. Belafsky at the Center include unsedated treatment of laryngeal polyps, leukoplakia, and papillomas, subglottic, tracheal, and esophageal strictures, and office-based vocal fold medialization. Dr. Belafsky’s primary research focus is the development of an artificial swallowing mechanism. He has created a medical device that can manually control the upper esophageal sphincter and is working on a comprehensive swallow propulsion system. He is also pursuing his interest in bloodless surgery through the use of radio frequency probes and non-contact lasers.
- CASE: 82 yo male presented with the chief complaint of solid food dysphagia and moderate dysphonia. He reported a 15lb weight loss over the past 18 months and 1 episode of pneumonia requiring hospitalization 5 months previous.
- PMHx: Hypertension, hypercholesterolemia, Parkinson’s disease
- PSurgHx: Inguinal hernia repair, rotator cuff repair
- ALLERGIES: None
- MEDS: Lipitor, Cardizem
- SOCIAL HISTORY: Retired Air Force Colonel, served in Vietnam War. No tobacco or illicit drug use. Social ETOH. Lives at home with his wife of 49 years. 3 children and 7 grand children. Good familial support.
- REVIEW OF SYMPTOMS: Solid food dysphagia, Hypertension, urinary frequency, weight loss, mild resting tremor, dysphonia
- SELF-RATINGS:
- PHYSICAL EXAM: Comprehensive head and neck examination unremarkable. Mild upper extremity resting tremor and mild bradykinesia. Oral motor examination unremarkable. Moderate breathy dysphonia.
- FEES: moderate laryngeal edema with underlying vocal fold atrophy, posterior commissure hypertrophy, mild arytenoid hyperemia. Pharyngeal strength and sensation appeared intact. There was significant post-swallow regurgitation with puree with no evidence of penetration or aspiration during the swallow.
- MBSE: Videofluoroscopic swallow study revealed evidence of a moderately obstructing cricopharyngeus muscle bar and an early Zenker Diverticulum. There was delayed pharyngeal transit time but no evidence of penetration or aspiration.
- TREATMENT RECOMMENDATIONS:
- Swallowing and voice therapy. Swallow for life program with iSwallow. EMST. LSVT. (Feel free to add to this).
- The patient was offered a cricopharyngeus muscle myotomy and a medialization laryngoplasty or an injection medialization of the vocal folds and a CP botulinum toxin injection. Because of his advanced age the patient desired an injection medialization and a CP botulinum toxin injection.
- WATCH MEDIALIZATION (0.4cc of calcium hydrozylapatite injected into each true vocal fold)
- WATCH BOTOX INJECTION (60 units of botulinum toxin injected into the cricopharyngeus muscle)
- OUTCOME: Post-therapy and Postoperatively the patient reported a significant improvement in voice and swallowing function. Repeat videofluoroscopy revealed improved bolus transit through the pharyngoesophageal segment with near complete resolution of the Zenker’s Diverticulum. WATCH EXAM
- FOLLOW-UP: He will be monitored closely for a progression of his dysphagia when the botulinum toxin wears off in 6-9 months. He will continue with his Swallow for Life Program.